UI Designers and UX Designers have numerous creative tasks that require knowledge, talent and imply the necessity to keep up with the latest trends and market needs. These seemingly twin roles involve many different duties, goals, missions, and responsibilities. On the other hand, they do have many things in common and some mutual objectives. Both UI and UX Designers have a distinctive ability to combine aesthetically pleasing features and content with effectiveness and usability.
There is a difference between UI and UX Designers and their tools and objectives. However, they blend perfectly with each other when it comes to uniting easy on the eye with functional & uncomplicated details and qualities.
There is a difference between UI and UX Designers and their tools and objectives. However, they blend perfectly with each other when it comes to uniting easy on the eye with functional & uncomplicated details and qualities. difference between UI and UX DesignersThere is a difference between UI and UX Designers and their tools and objectives. However, they blend perfectly with each other when it comes to uniting easy on the eye with functional & uncomplicated details and qualities.
What is a User Interface (UI) design
User Interface is meant to communicate a brand’s values, and help the users understand the product, interact with it quickly and efficiently while having a pleasant experience. UI simplifies the way towards accomplishing users’ goals.
UI design stands for the process Designers set to build interfaces in software or computerized devices, while simultaneously focusing on appearances and style. UI Designers strive to create interfaces that users find comfortable to use.
What is User Experience (UX) Design
User experience (UX) design is the process designers use to create products that produce meaningful and consistent experiences for users. UX involves the design of the whole process of obtaining and integrating the product, including aspects of branding, design, usability, and purpose.
Simply put, UX design is the process of designing (digital or physical) products that are pleasing and refreshing to interact with, and easy to use. UX Designers strive to improve the experience that people have while interacting with a product. They are making sure users can recognize the products’ value.
UX VS. UI – the key differences
So, here’s what everyone knows, and we’re still going to repeat it, just to make a point – UX stands for User Experience, and UI stands for User Interface. These definitions don’t make it any clearer, right? The knowledgeable audience might spot a difference, but they’d also struggle to explain it and to draw a line between the two.
Typically paired as UX/UI design, these terms create the perfect combination, which is highly demanded in the tech industry. UX/UI Designers make remarkable websites, applications, games, or any other kind of digital products. Still, the loose usage of the terms UX and UI makes these two interchangeable, which makes it difficult to untangle the gorgeous mess they create.
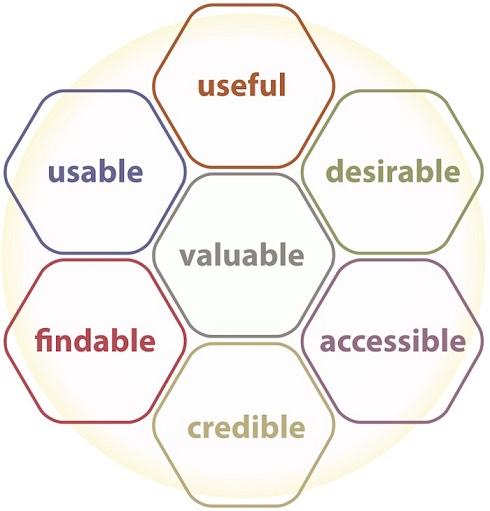
UX design is associated with usability, usefulness, credibility, accessibility, findability, being valuable, and desirable.
UX design primarily includes analysis to learn things like customer pain points, market gaps, and researching competitors. Besides concentrating on an extensive comprehension of users and potential market demands, UX considers the business aims and goals to build products that align with the company’s ideas. UX’s most excellent practices enrich user interactions with products and their attitudes towards it.
UI design is concentrated on the appearance and layout — it determines how every element of the product should look, which includes buttons, text, images, and every other visual element users interact with.
UX decides how the interface works and how people interact with it; UI formulates an interface’s looks and sense.
So, we can conclude that UX makes an interface useful and usable, while UI makes it beautiful. A beneficial and serviceable product meets a requirement that is not already being met in the market. The research process of a UX designer includes doing a competitive study and analysis, developing personas, and developing a product that will be relevant to a targeted customer industry or area. Usability is confirmed through testing during the entire life-cycle of the product.
The next step is to prototype and test user flows and wireframes. Once it’s done, it is the UI designer’s part to make them visually gratifying. This process includes picking a color scheme and typography that will be simultaneously good-looking and uncomplicated to use. Nevertheless, color choices, typography, and interactions can’t be based on the designer’s individual inclination. Instead, they’re based on precisely articulated goals distinct to the personas developed by the UX designers. UI designers achieve a visual structure that serves as a guide for users.

UX drives users to accomplish their goals; UI creates heartfelt connections
UX asks the relevant questions about users, their needs, and what exactly they’re looking for. UX implies observing people, interviewing them, and making prototypes. A bit of guerrilla testing might also be part of this process to determine the value propositions.
Personalizing a website, an app, or whichever digital product you have is what creates firm bonds, leads to consumers’ loyalty, and makes them come back for more. It’s UI’s turn to make sure a personal connection is made.
UX is usually done first
As if defining differences between UX and UI wasn’t tricky enough, we’re also in a bit of a chicken and the egg situation here. Typically, focusing on the UX design and research is the initial move while determining what kind of a product should be built. UX designers conduct the research that validates or nullifies original product ideas and directs the development of the product. Nonetheless, the designing process is often not a linear path, and it depends on several factors. The steps might vary depending on the person or the designing team in charge.
User Experience design represents a more extensive set of areas and duties
User experience design is becoming more popular daily, and it brings a wide range of advantages to countless products. Not only businesses with a web presence need and understand its value. Many other organizations that develop their products or provide services need to grasp their users’ necessities and requirements.
On the other hand, User Interface’s name says it all – its purpose revolves around user interfaces. However, this doesn’t indicate UI is restricted solely to the graphical user interfaces of computers, tablets, and mobile devices. We can find interfaces on multiple other products nowadays.

UX designers’ role
UX designer focuses on building a product’s structure, flow, and functionality. Mainly, they work jointly with marketers, BA specialists, and product teams, which helps them fully recognize user demands.
UX Designer Principal Responsibilities
- User Analysis
- Competitor Analysis
- Product Structure and creating an adequate strategy
- Prototyping
- Testing/Iteration
- Planning
- Wireframing (content layout and functionality)
- Analytics and Execution imply cooperation and communication with Development teams, collaboration with UI Designers, analysis and iteration, tracking goals, and integration.
UI designers’ role
UX and UI Designers consider and plan the structure of a project. UI designers create high-fidelity layouts with responsive guidelines by following the visual identity, style guides, and UI kits. After it’s done, they define animations and transitions.
UI designers create comprehensive style and reference guides to help developers understand the scheme. UI designers collaborate closely with developers. They test the product and strive to give precise feedback about it.
UI Designer Principal Responsibilities
- Physical appearance and Feel: Meeting the goals and providing a personalized and appealing design includes taking care of branding and graphic developing, User Guides/Storyline, Design Research, Customer Analysis
- Responsiveness and Interactivity: Compliance to each device and compatibility with various screen sizes, interactivity and animation
- Implementation with Developers
- UI Prototyping
UX and UI are Yin & Yang of digital product design
Even though both are following a mutual business goal, UX and UI need different processes, skills, and preferences. UX design is based on a user’s desires and needs, and UI design is based on the analysis, guidance, and requirements of the UX designer. UX is closely connected to project and product management, while UI relies on more artistic components.